Table of Contents
- Thermal Bridging and Roof Thermal Breaks
- Roof Building Envelope Performance
- Condensation Risks
- Roof Connection Structural Thermal Break
- Using ClimaSpec Roof Connection Thermal Breaks
Thermal Bridging and Roof Thermal Breaks
Evolving construction practices, stringent energy standards, and the demand for more outdoor amenity space create modern challenges for energy-efficient building envelope design. Roofs, in particular, create numerous challenges in maintaining a consistent thermal barrier due to certain connections that are directly fixed to the main building structure and bypass the roof insulation line. Some examples of roof penetrations are roof posts, roof anchors, davits, and dunnage.
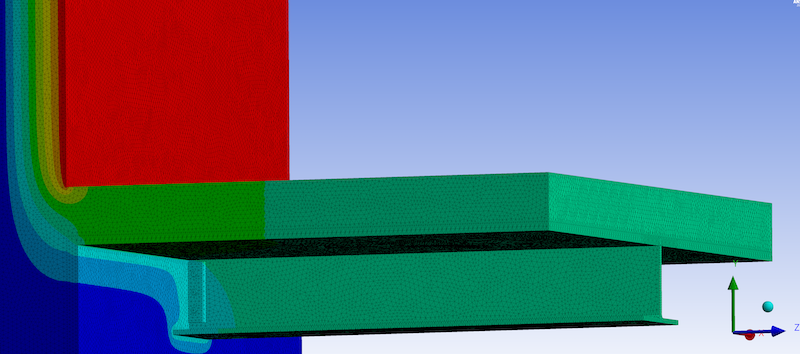
To ensure an effective energy roof design that successfully improves the building envelope performance and reduces condensation risks, it is important to reduce thermal bridging by thermally isolating roof connections with structural thermal breaks
Roof Building Envelope Performance
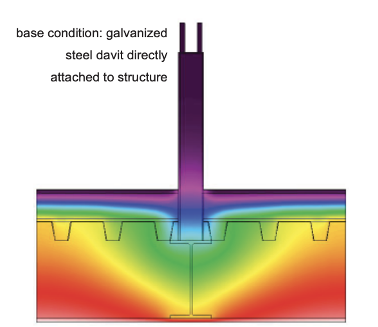
Certain building materials have different thermal properties, and their selection can reduce the R-Value of a roof. For example, highly conductive roof connections such as steel that are directly connected to the main building structure and bypass the insulation line. Using structural thermal breaks to thermally separate the interior and exterior building components is good practice for reducing the thermal bridge and increasing the roof building envelope performance.
Note: It has been shown through thermal modeling that using a steel end plate design with structural thermal breaks can reduce the unwanted heat loss at the assembly by over 50%.
Condensation Risks
Condensation in a roof building envelope occurs when warm, moist air comes into contact with a surface that is at or below its dew point temperature.
Note: The dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with moisture, leading to the condensation of water vapor.
Insufficient insulation methods can lead to heat loss through the roof structure (thermal bridging), and cause significant temperature differentials between the indoor and outdoor environments, contributing to increased condensation risks.
Building designers must carefully consider these factors to create an effective and moisture-resistant roof building envelope.
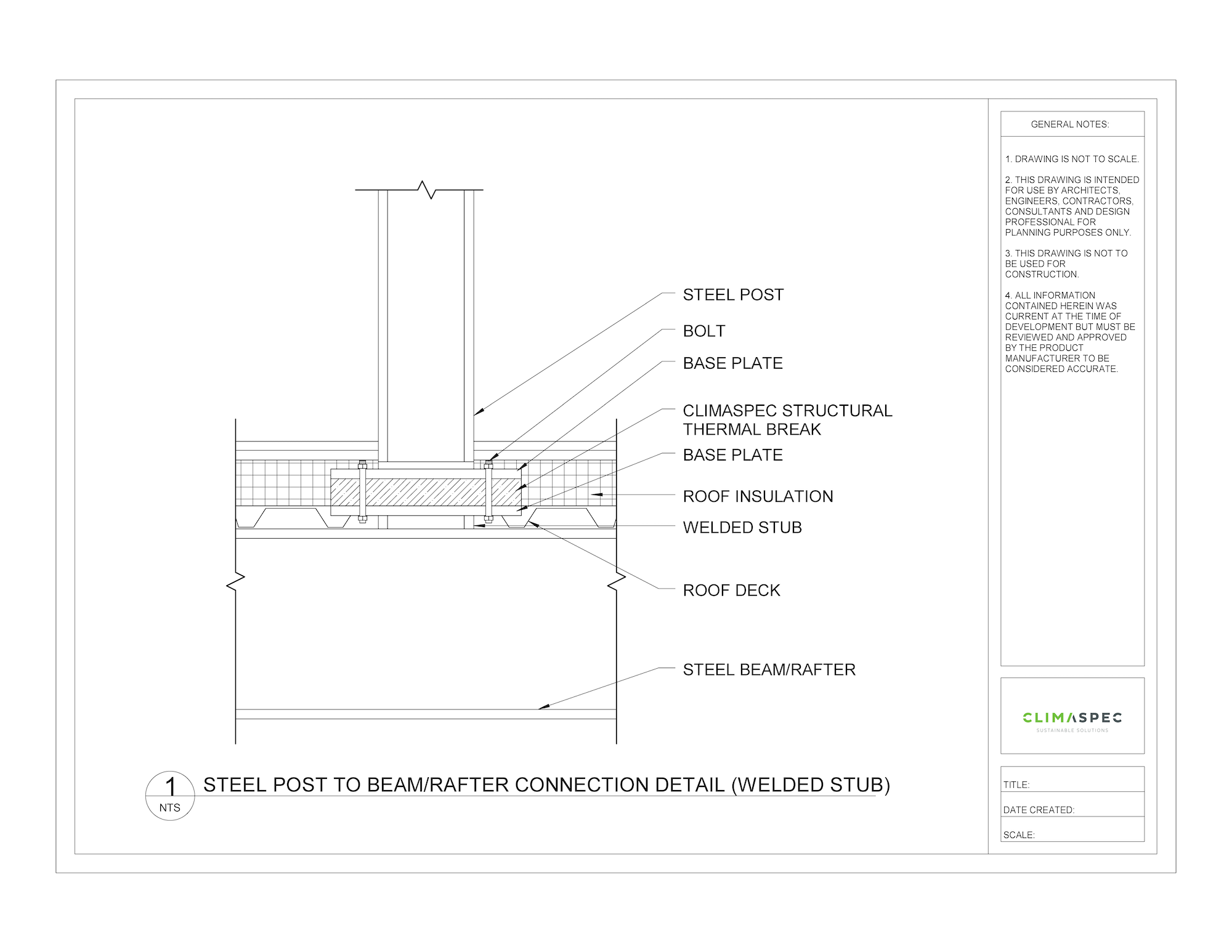
Roof Connection Structural Thermal Break
The structural thermal break should be installed between the base plate of the exterior building component and the interior building framing. Therefore, creating a thermal barrier and reducing the heat transfer through the roof building envelope.
Structural thermal breaks are prefabricated to match the dimensions and hole layout of the base plate that is being thermally separated. Also, numerous thicknesses are available depending on the project’s structural and thermal requirements. If required, the structural thermal break dimensions can be oversized to allow for increased structural capabilities.
Using a bolt-through connection safely secures the structural thermal break to the connection and although the surface area of the base plate has now been thermally separated, smaller thermal bridges still occur due to the heat transfer through the bolts. If required, to minimize the thermal bridging even further, stainless steel bolts and thermal washers can be used to reduce the heat transfer through the bolts.
Below are some examples of how structural thermal breaks can be integrated into roof connections such as roof posts, roof anchors, dunnage, and davits.
Note: Remember, structural thermal breaks can be used for both steel and concrete framing roof connections.
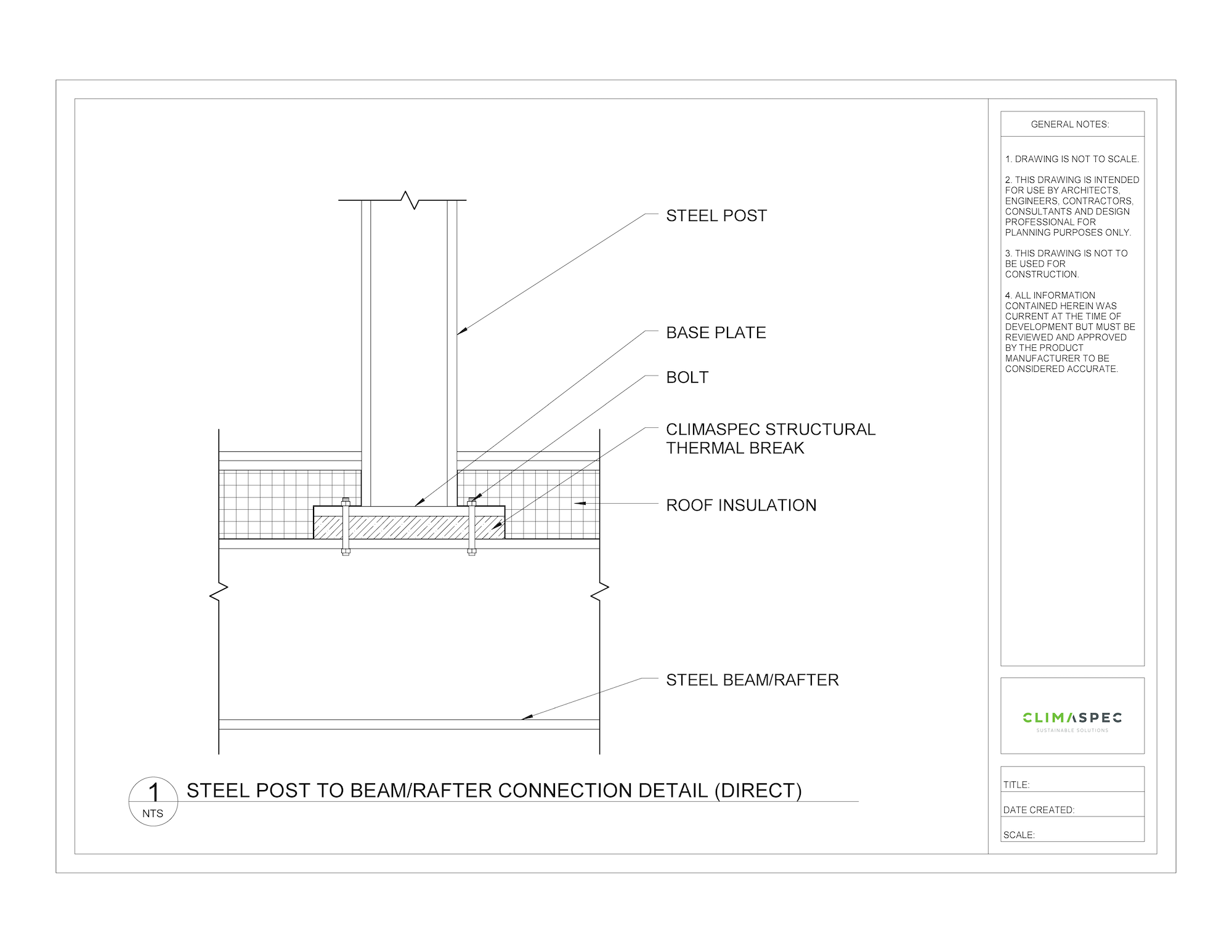
Regarding R-Values, structural thermal breaks are just like other insulation materials. The thicker the insulation the higher the R-Value. However, using larger thicknesses leads to larger bolt lengths, so it is important to ensure the extra bolt length capabilities are included in structural calculations. Fortunately, structural thermal breaks are specifically designed to ensure both thermal and structural requirements are met.
Note: Simply reducing the thermal break thicknesses or using a welded stub detail are both design options when the thermal break thickness needs to be reduced.
Using ClimaSpec Roof Connection Thermal Breaks
Structural thermal breaks play a crucial role in improving the roof building envelope performance by minimizing thermal bridging and heat loss. This leads to reduced condensation risks, and improved roof durability and thermal effectiveness.
ClimaSpec Structural thermal breaks are easily integrated into a variety of roof connections due to their material properties and adaptiveness to project thermal and structural requirements.
ClimaSpec Structural thermal breaks are adaptable in a variety of roof connections due to their optimum thermal and structural capabilities. Making them an efficient sustainable solution for high-performing roofs.
Contact ClimaSpec today to get a fast quotation or thermal bridging guidance for your roofing construction projects.