Table of Contents
- American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE)
- Building Requirements
- ASHRAE 90.1 Thermal Bridging
- Mitigating Thermal Bridges
- Understanding Thermal Bridging
- Importance of Recognizing Thermal Bridging
- ASHRAE 90.1-2022 and Thermal Bridging Highlights
- Increasing Sustainable Design Requirements
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE)
ASHRAE Standard 90.1, is a widely recognized and influential energy standard for buildings. Developed by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), this standard provides guidelines and minimum requirements for the energy-efficient design and construction of commercial and high-rise residential buildings
Building Requirements
ASHRAE 90.1 is designed to establish the baseline for energy performance in buildings, with the overarching goal of reducing energy consumption and promoting sustainability. It covers various aspects, including building envelope requirements, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, lighting systems, and other energy-related components. The standard is periodically updated to incorporate advancements in technology, construction practices, and energy efficiency research, ensuring it remains a relevant and effective tool for promoting responsible energy use in the built environment.
ASHRAE 90.1 Thermal Bridging
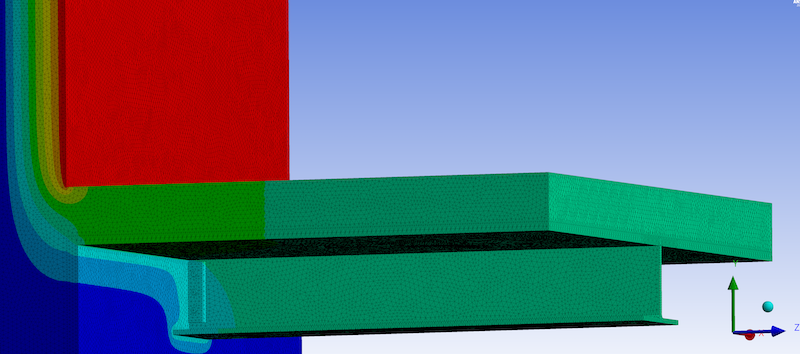
One notable inclusion in ASHRAE 90.1-2022 is the recognition of some types of thermal bridges, in particular, linear thermal bridges and some point thermal bridges. As well as an approach that integrates guidelines and mitigation strategies.
Additionally, there is an introduction of specific calculation methods tailored to assess the impact of thermal bridging. These methods take into account factors such as material conductivity, the geometry of building components, and other relevant parameters. By incorporating these considerations, the standard aims to provide a more accurate representation of a structure’s thermal performance.
Mitigating Thermal Bridges
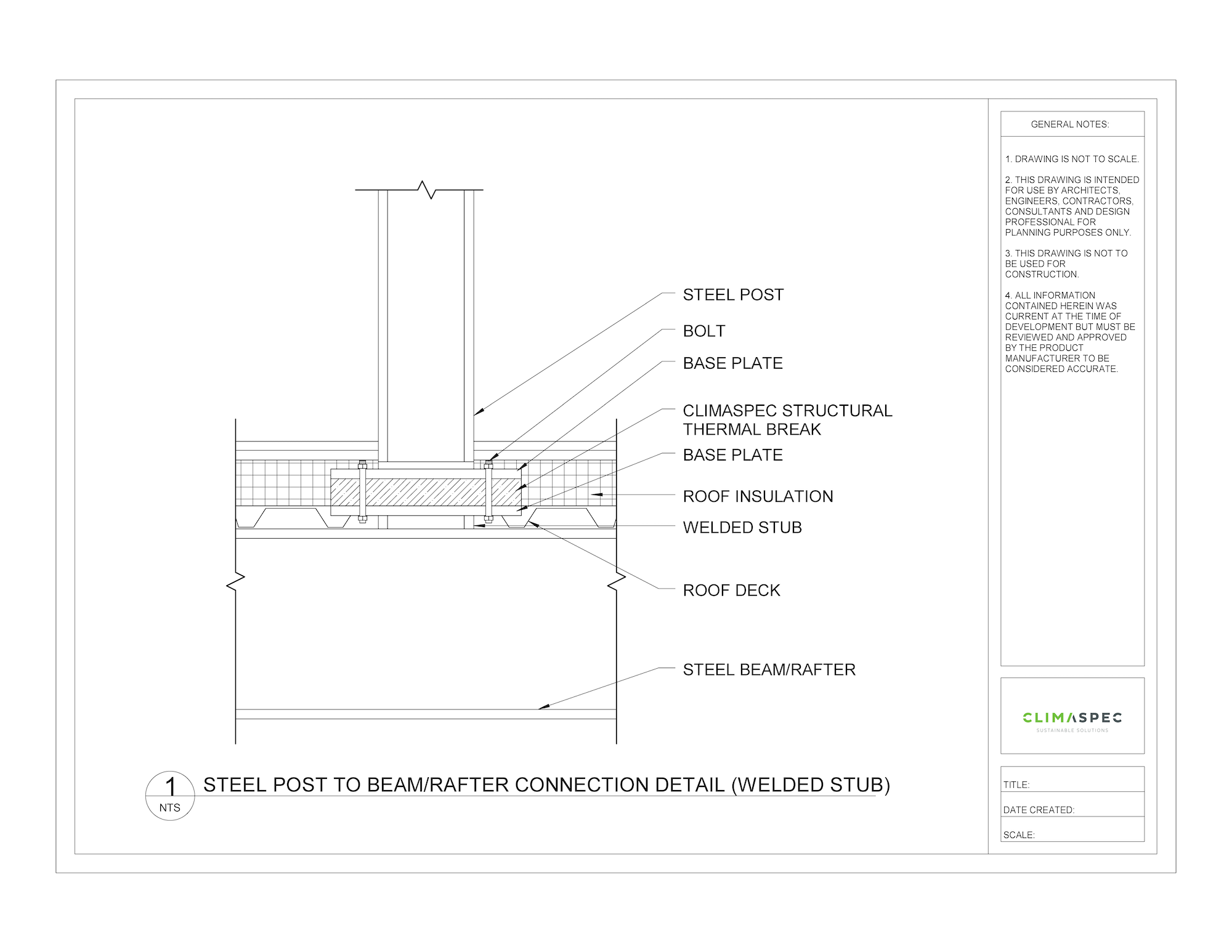
ASHRAE 90.1-2022 goes further and provides the performance requirements for mitigated linear and point thermal bridges. A thermal bridge that is over the mitigated value will require to be reduced unless an exception applies.

Thermal bridge values need to be confirmed to be compliant so using structural thermal breaks, enhanced insulation techniques, or employing alternative construction methods to minimize heat transfer through building elements should be employed. These strategies align with the overarching goal of the standard to improve the building energy efficiency.
Understanding Thermal Bridging
Thermal bridging, also referred to as a cold bridge, occurs when a highly conductive material allows heat to flow through a building envelope more easily than the surrounding insulation. This can lead to energy inefficiency, increased heating and cooling costs, and potential comfort issues for building occupants. Traditional building designs often underestimate the impact of thermal bridging, resulting in structures that are less energy-efficient than calculated.
Importance of Recognizing Thermal Bridging
The significance of recognizing thermal bridging lies in its direct correlation to a building’s overall energy performance. Ignoring thermal bridging can result in overestimating a structure’s thermal resistance and, consequently, lead to higher energy consumption. By acknowledging and addressing thermal bridging, ASHRAE 90.1-2022 aims to promote more accurate assessments of building energy use and, ultimately, enhance overall energy efficiency.
ASHRAE 90.1-2022 and Thermal Bridging Highlights
The inclusion of thermal bridging in ASHRAE 90.1-2022 highlights the growing pressure to ensure buildings are being designed and built in a more energy efficient way. Here are some key aspects covered by the updated standard:
- Performance-Based Approach: ASHRAE 90.1-2022 adopts a performance-based approach to assess thermal bridging. Instead of relying solely on prescriptive measures, the standard allows for a more flexible evaluation of a building’s thermal performance.
- Thermal Bridging Calculation Methods: The code introduces calculation methods for determining the impact of thermal bridging. These methods consider factors such as material conductivity, geometry of building components, and other relevant parameters to provide a more accurate representation of a structure’s thermal performance.
- Design Methods: ASHRAE 90.1-2022 requires mitigating certain thermal bridges. Design methods such as structural thermal breaks can help ensure thermal bridge performances are met.
- Increased Stringency: The new standard sets more stringent requirements for thermal performance, reflecting a commitment to raising the bar for energy efficiency in building design. This includes revised insulation requirements and a focus on reducing overall heat loss.
Increasing Sustainable Design Requirements
The increased thermal performance requirements within ASHRAE 90.1-2022 underlines a commitment to improving the energy efficiency of building design. By recognizing the impact of thermal bridging and providing guidelines for its assessment and mitigation requirements, the updated standard encourages designers, architects, and engineers to create buildings that meet new energy efficiency expectations. Once States and municipalities adopt or adapt the newest revisions of the IECC and ASHRAE 90.1 energy codes, the closer we are toward achieving Net Zero emissions. Until then, it is paramount that buildings are designed beyond energy codes, to ensure target energy goals are met.
Contact us today to discuss how ClimaSpec Structural Thermal Breaks can help reduce thermal bridging within your building envelope designs.