Table of Contents
- What is Cold Storage?
- Energy Challenges of Cold Storage
- Thermal Bridging Cold Storage
- Cold Storage Structural Isolation Blocks
- Cold Storage Column Base Structural Isolation Blocks
- Insulated Metal Panel (IMP) Structural Isolation Blocks
- Validating Thermal Performance Improvements
- To Summarize Cold Storage Structural Isolation Blocks
What is Cold Storage?
A cold storage warehouse, is a specialized storage facility designed to maintain specific temperature and humidity conditions for the storage of perishable goods, ensuring their preservation and quality. Cold storage warehouses can be categorized into different types of climate controlled warehouses depending on the the specific temperature ranges are used.
To qualify as freezer storage by USP standards, temperatures in a storage unit must fall within the -4°F to 14°F range. Cold storage, which is also referred to as refrigerated storage temperatures must not exceed 46°F. “Cool” storage is defined between 46°F and 59°F. Some cold storage facilities might have multiple temperature zones within the same warehouse, allowing for the storage of various goods with distinct temperature requirements.
Energy Challenges of Cold Storage
Cold storage facilities face several challenges that can impact their operational efficiency, the quality of stored products, and overall effectiveness in the supply chain. Also, maintaining low temperatures within cold storage facilities requires significant energy consumption. The high electricity costs and the environmental impact associated with energy use can pose challenges for facility operators. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices is crucial to mitigate these issues.
Additionally, consistent temperature control is essential for preserving the quality of stored products. Temperature fluctuations, whether due to airflow, reloading requirements for goods, or inadequate insulation methods, can lead to spoilage, loss of product quality, and compliance issues with industry regulations. Condensation and humidity levels are also critical in cold storage facilities, excessive moisture can lead to the formation of ice, mold growth, and deterioration of materials.
Thermal Bridging Cold Storage
Thermal bridging can occur in various areas within cold storage facilities. In other words, where there is a direct pathway for heat to flow through building components, this compromises the overall insulation and energy efficiency of the connection design. Inadequate insulation methods can contribute to increased energy consumption, uneven temperatures, and reduced overall insulation efficiency. Identifying and addressing thermal bridging is crucial for maintaining consistent internal temperatures and reducing energy consumption.
Cold Storage Structural Isolation Blocks
Cold storage structural isolation blocks, also known as ClimaSpec Structural Thermal Breaks are an engineered solution specifically designed to minimize thermal bridging. They do this by interrupting the transfer of heat through structural elements that penetrate the insulation line of a cold storage warehouse.
ClimaSpec Structural Thermal Breaks can be designed into several locations of structural connections within the insulation line of cold storage facilities. By mitigating thermal bridging, optimal energy efficiency and temperature control design can be achieved.
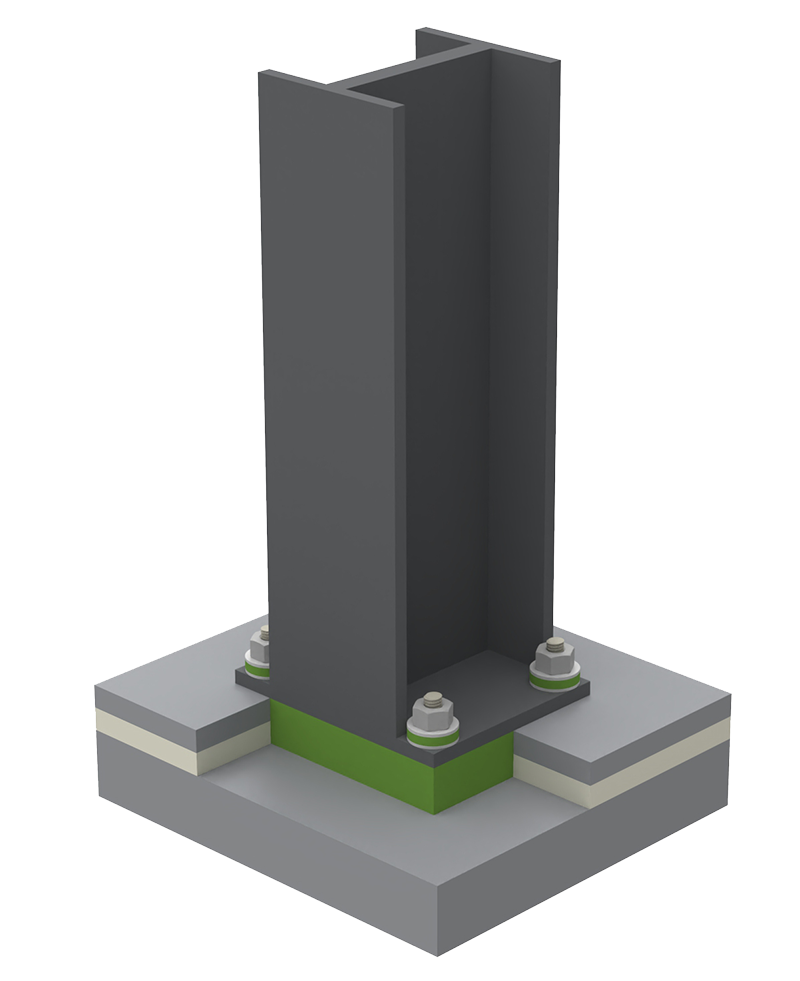

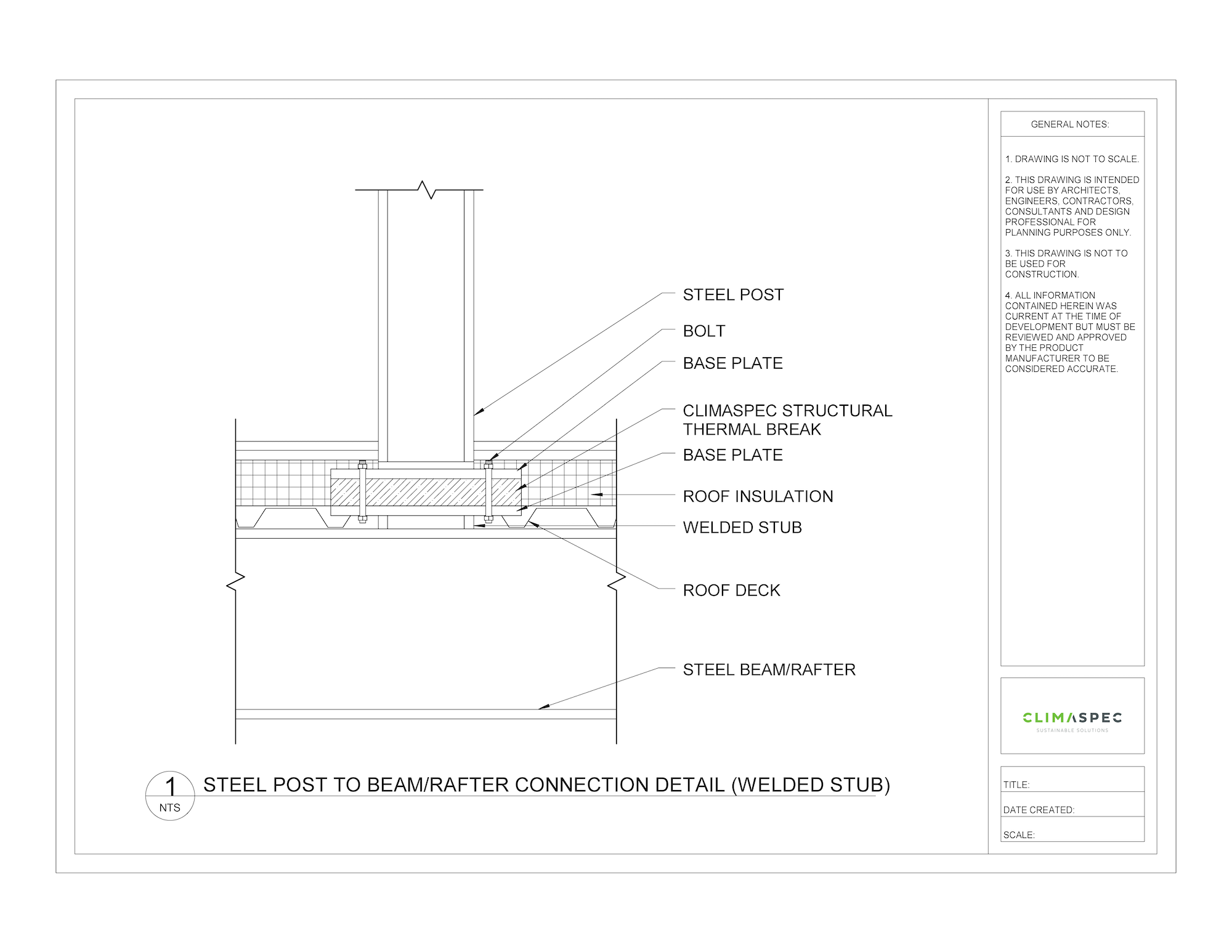
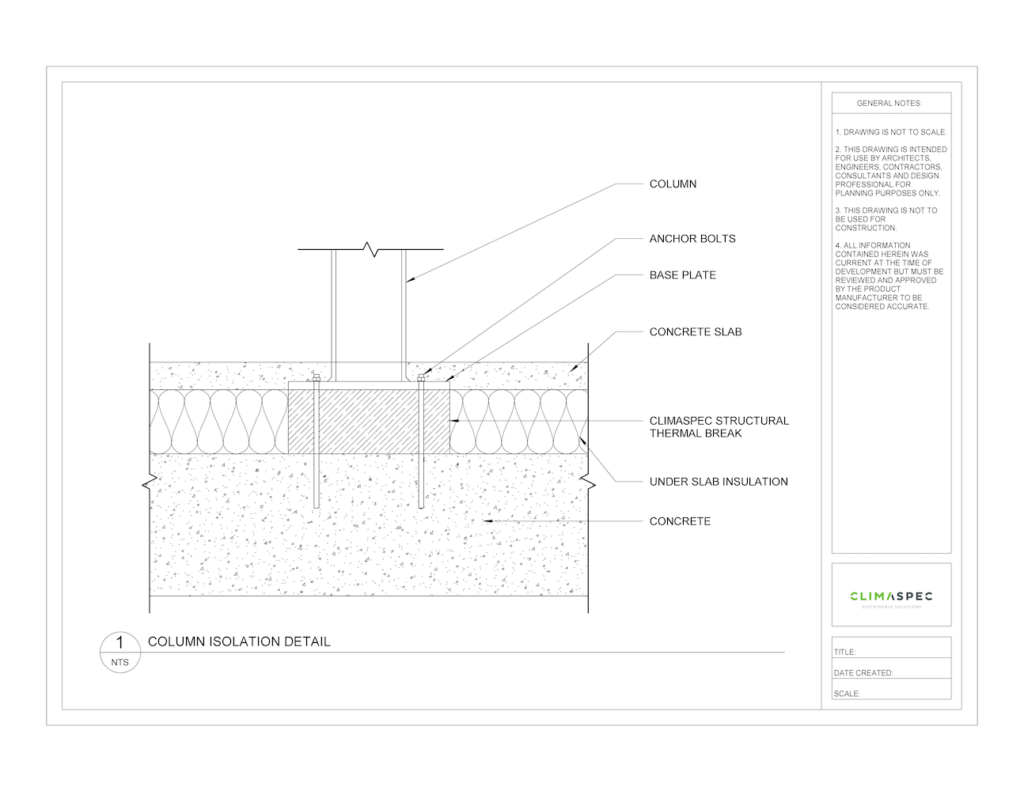
Cold Storage Column Base Structural Isolation Blocks
Consider a cold storage facility with structural columns supporting the framing. The column base penetrates the floor insulation line with a steel column, which is a highly conductive material and creates a thermal bridge allowing heat transfer between the temperature regulated interior and the external environment. Using ClimaSpec CI Structural Thermal Breaks to thermally isolate the column base from the concrete minimizes unwanted heat loss and improves the thermal performance of the cold storage facility. ClimaSpec CI is prefabricated to size to accommodate the column base size and structural loads. Holes are also predrilled for easy installation at the anchor bolt locations.
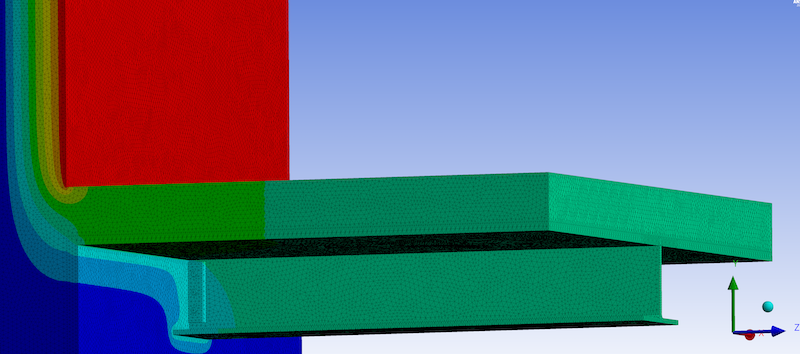
Insulated Metal Panel (IMP) Structural Isolation Blocks
Thermal bridges can also occur when attaching equipment or racking through the insulated metal panel (IMP) floor for walk-in freezers and coolers. ClimaSpec CI can be strategically installed into the IMP at the locations where the equipment or racking would bypass the insulation line when being fixed to the floor, providing the necessary thermal and structural requirements when thermally separating the equipment or racking from the floor.

Validating Thermal Performance Improvements
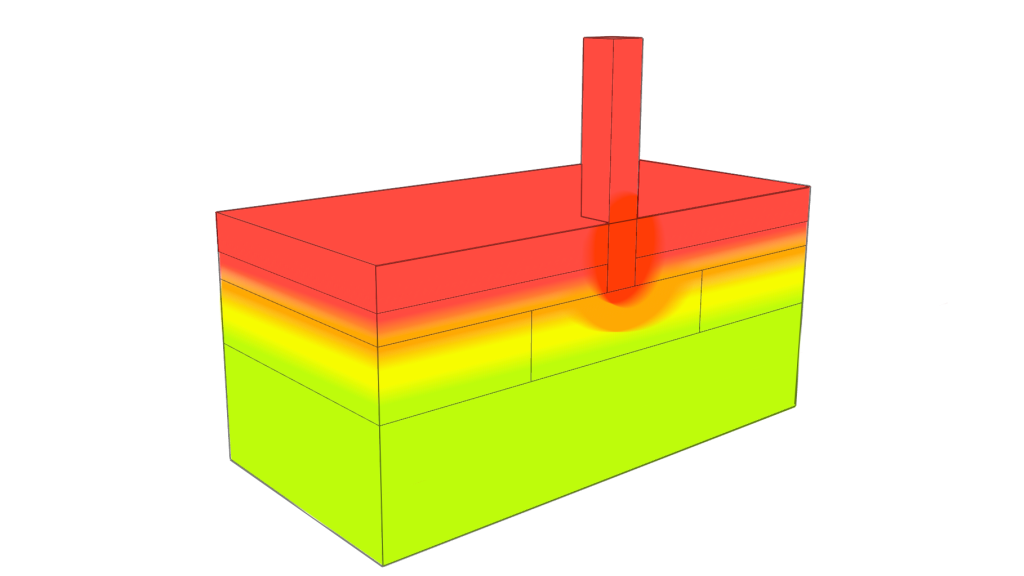
It is important to be able to show how insulation methods and designs contribute to increasing the energy efficiency of a cold storage facility. This is why thermal modeling can be used to demonstrate the thermal performance and energy increases when minimizing thermal bridging with ClimaSpec Structural Thermal Breaks. Through thermal modeling, connection designs can simulate the behavior of a building’s thermal envelope under different conditions, helping to understand how insulation, materials, and the structural elements that bypass it contribute to the energy efficiency of the cold storage facility. Here are some benefits of thermal modeling when demonstrating the increase in thermal efficiencies:
Assessment of Thermal Bridges: Thermal modeling allows for a detailed analysis of potential thermal bridges within a building envelope. By inputting the properties of the structural components that bypass the insulation line, thermal modeling can identify areas where heat transfer might occur.
Comparison of Insulation Scenarios: Thermal modeling also enables designers to compare different insulation scenarios, including the presence or absence of structural isolation blocks. By modeling the connection with and without the blocks, the impact on overall heat transfer and thermal bridging can be assessed. This comparison provides a quantitative measure of the thermal efficiency increase associated with the use of ClimaSpec CI Structural Thermal Breaks.
Surface Temperature Prediction: Thermal modeling predicts surface temperatures across different building components. By comparing these predicted temperatures to the dew point, designers can identify locations where surfaces might become cold enough to cause condensation. This insight helps in targeting areas that require additional insulation methods.
To Summarize Cold Storage Structural Isolation Blocks
Cold storage structural isolation blocks also known as ClimaSpec CI Structural Thermal Breaks improve the energy efficiency performance of cold storage facilities by minimizing thermal bridging at load-bearing connections. Design improvement energy efficiencies can be simulated with the use of thermal modeling, and the information can be used for more accurate overall building energy performance calculations.
If you would like to discuss how ClimaSpec Structural Thermal Breaks and thermal modeling can improve your cold storage connections, contact us today to speak with a thermal bridging expert.