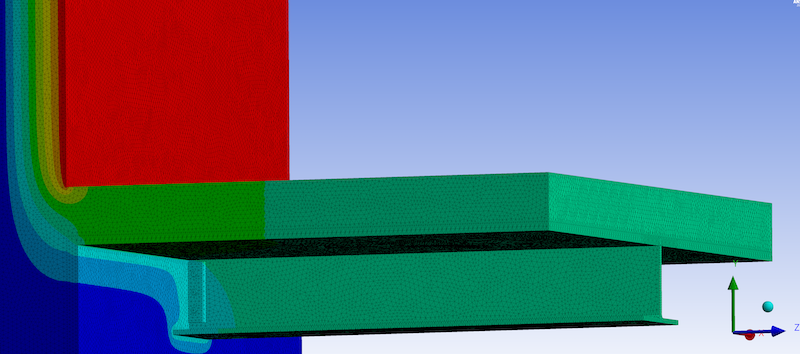
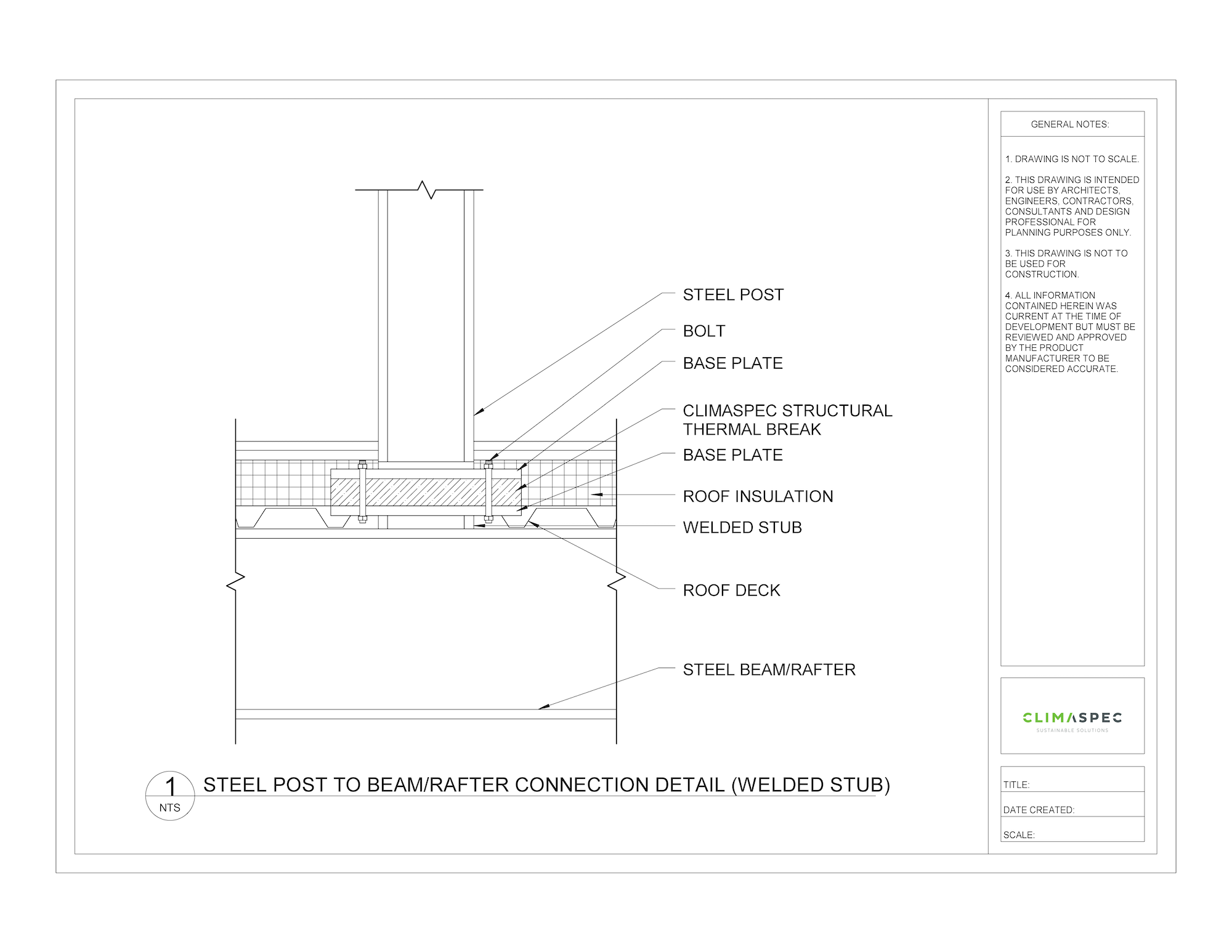
In the pursuit of a sustainable future, the United Nations has outlined 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to address global challenges and improve the quality of life for all. Target 9 specifically focuses on building resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and fostering innovation. One method of achieving this target is the integration of structural thermal breaks in construction practices. In this post, we will discuss how structural thermal breaks contribute to the realization of Global Goals Target 9.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Structural Thermal Breaks
- Reducing Energy Consumption
- Mitigating Climate Change
- Enhancing Building Resilience
- Fostering Innovation in Construction
- Implementing Structural Thermal Breaks
- Building a Sustainable Future
Understanding Structural Thermal Breaks
Structural thermal breaks are a type of load bearing insulation that are incorporated into the building envelope to minimize heat transfer between structural components, such as slabs and balconies, that penetrate the thermal insulation line. Traditional construction methods often neglect the impact of thermal bridging, which can result in energy inefficiencies, increased carbon emissions, and compromised building performance.
Reducing Energy Consumption
One of the key benefits of structural thermal breaks is their ability to enhance the thermal performance of buildings. By minimizing heat transfer through structural connections, thermal breaks reduce the overall energy consumption required for heating and cooling. This aligns with the SDG target of building resilient infrastructure by promoting energy-efficient solutions that contribute to the mitigation of climate change.
Mitigating Climate Change
The construction industry is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, and addressing thermal bridging is a crucial step in reducing its environmental impact. Structural thermal breaks help meet Target 9 by reducing energy consumption, thereby building lowering carbon emissions. This aligns with the broader global goals of combating climate change and transitioning towards a more sustainable, low-carbon economy.
Enhancing Building Resilience
Resilient infrastructure is a cornerstone of Target 9, and structural thermal breaks play a role in enhancing the durability and longevity of buildings. By preventing thermal bridging, thermal breaks contribute to the overall structural integrity of a building, reducing the risk of moisture-related issues, corrosion, and other structural problems. This not only extends the lifespan of the infrastructure but also minimizes the need for maintenance and repairs, aligning with the goal of building sustainable and resilient structures.

Fostering Innovation in Construction
Innovation is also a key component of Target 9, and the integration of structural thermal breaks represents a progressive step in the construction industry. As architects, engineers, and builders adopt more sustainable technologies, an increased development of innovative solutions that prioritize energy efficiency and reducing building carbon footprint will occur. This aligns with the UN’s call to promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, driving positive change within the construction sector.

Implementing Structural Thermal Breaks
The implementation of structural thermal breaks not only aligns with Global Goals Target 9 but also generates a ripple effect across various interconnected sustainability objectives. By reducing energy consumption in buildings, thermal breaks contribute to Goal 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and Goal 13 (Climate Action), creating a more energy-efficient and environmentally conscious built environment.
Furthermore, the adoption of structural thermal breaks fosters collaboration and knowledge-sharing within the construction industry. As professionals exchange insights and experiences related to sustainable building practices, they contribute to Goal 17 (Partnerships for the Goals), emphasizing the importance of collective efforts in achieving the UN’s overarching sustainability agenda.
Building a Sustainable Future
As we strive for a sustainable and resilient future, it is essential to recognize the significance of sustainable construction design methods, such as structural thermal breaks that contribute to the broader vision of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals.