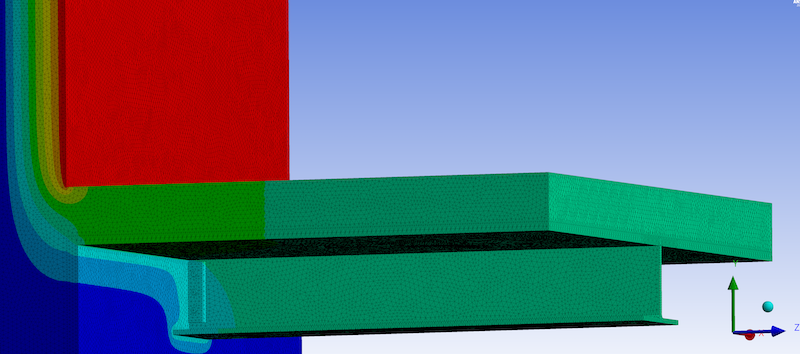
Table of Contents
- What are Masonry Shelf Angles?
- Masonry Shelf Angle Inefficiencies
- Masonry Shelf Angle Structural Thermal Breaks
- Masonry Thermal Break Size
- Bolt Selection and Improvements
- Design Considerations
- Simple Installation
- Information Required for Pricing
What are Masonry Shelf Angles?
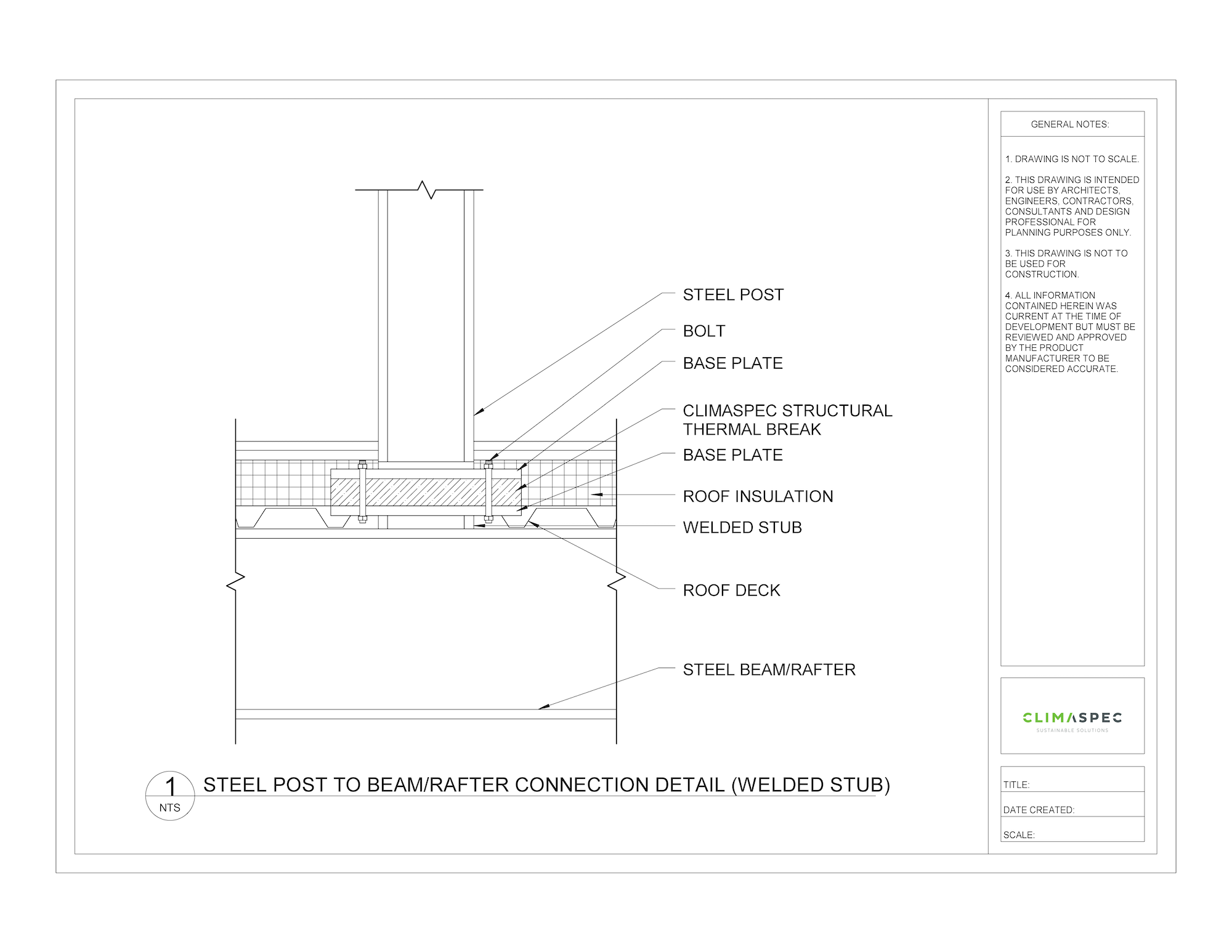
Masonry shelf angles, also known as support angles or brick angles, are commonly used to allow for movement due to growth and shrinkage between the masonry and structural framing. The relieving angle is fixed to a structural member for support and commonly has additional support along its length. The key focus here is how the shelf angle is fixed to the structural framing and how this is an important part of the connection design.
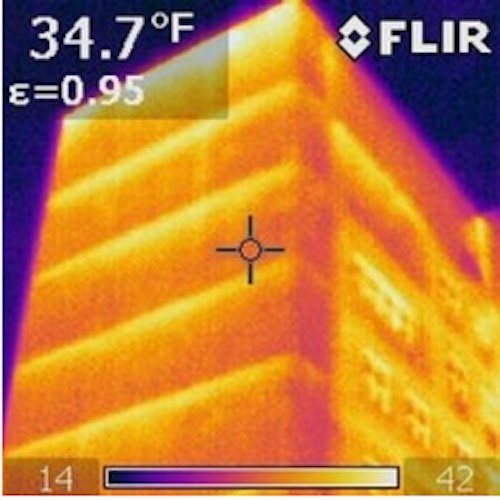
Masonry Shelf Angle Inefficiencies
Masonry shelf angles are commonly made of steel, which, while durable, has a higher thermal conductivity than the surrounding masonry or insulation materials. As a result, shelf angles, provide a continuous connection between the masonry veneer and the structural framing of the building. This continuity can create the direct transfer of heat, allowing heat to move between the building envelope. In turn, reducing the overall thermal resistance of the building envelope.
Masonry Shelf Angle Structural Thermal Breaks
Structural thermal breaks are designed to interrupt the flow of heat through building components, mitigating thermal bridging, and improving the overall energy efficiency of structures. By thermally separating the shelf angle from the structural framing, a reduction in unwanted heat loss occurs, in turn increasing the building envelope performance.
Structural thermal breaks for masonry shelf angles can be used in both concrete and steel structural framing applications, making them a viable option for an array of masonry shelf angle designs where thermal bridging occurs.
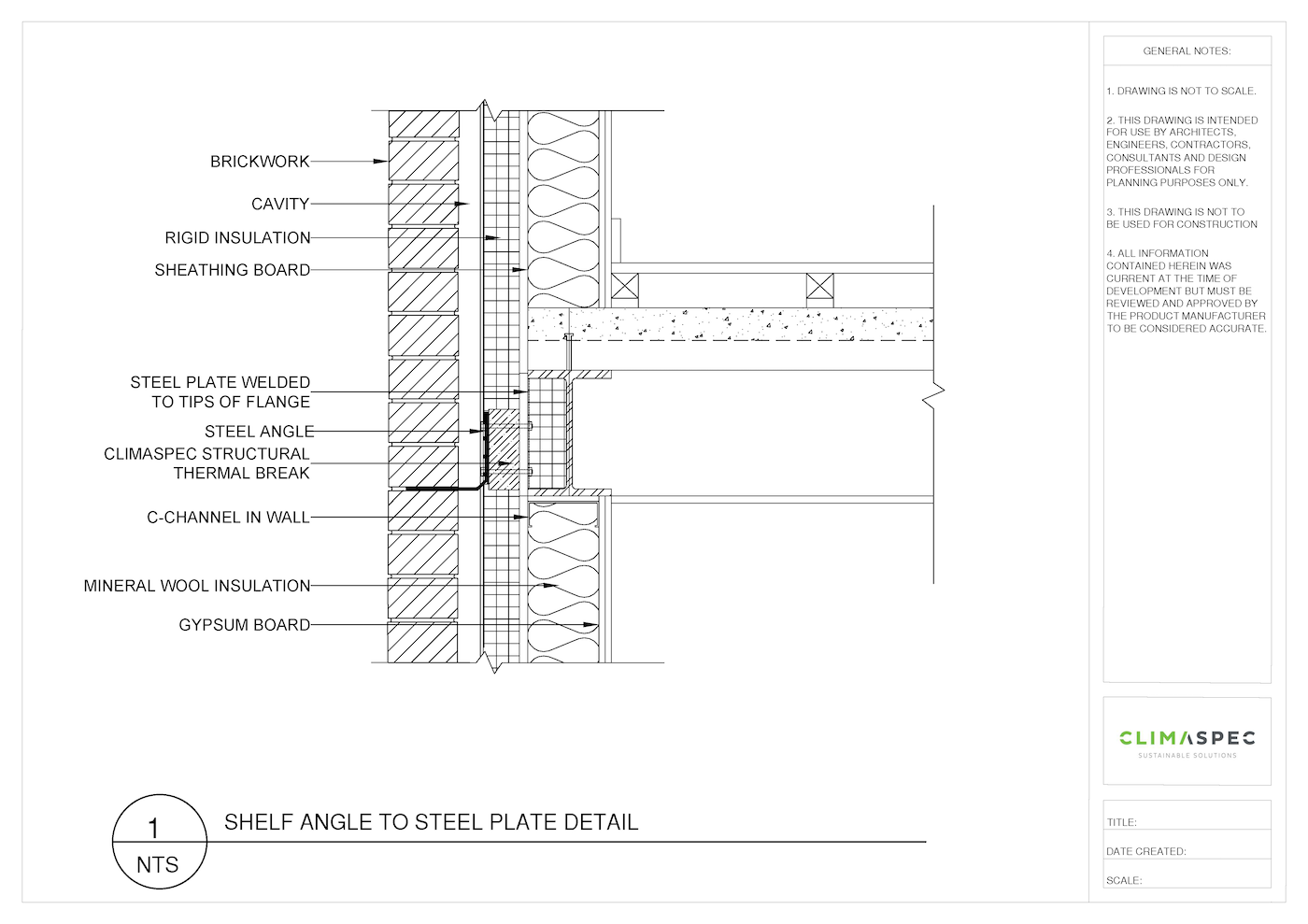
Masonry Thermal Break Size
The size and configuration of the masonry shelf angle structural thermal break depend on various factors, including the shelf angle size, the structural framing size and material type, the thermal efficiency requirements, as well as the structural design considerations at the shelf angle to the structural framing connection.
Each construction project is unique, and customization is key to achieving optimal results. Collaborate with structural thermal break manufacturers to customize the thermal break to match the dimensions and design specifications of the masonry shelf angles. This includes ensuring accurate dimensions and thermal break thicknesses, as well as the bolts or fixings being used for the specific application.
Bolt Selection and Improvements
Make sure to connect the structural thermal breaks to both the masonry shelf angles and the structural framing of the building using a through-bolt connection. The correct bolt ensures that the thermal breaks effectively support the load at the attachment connection while also interrupting thermal bridging. Standard steel bolts are used for steel angles to steel framing connections. Whereas anchor bolts are frequently used for steel angle to concrete structural framing connections.
Stainless steel bolts can improve the thermal performance of the shelf angle connections when used instead of standard steel bolts, however, it is important to check if the structural capabilities of the stainless steel bolts will meet the structural connection requirements.
Design Considerations
Collaborate with structural thermal break experts to ensure that the chosen structural thermal breaks are compatible with the specific design requirements of the masonry shelf angles. Load-bearing capacity, material compatibility, and the overall thermal performance objectives are the main areas of consideration.
Load-bearing considerations for structural thermal breaks at masonry shelf angles in particular are crucial in ensuring the structural integrity of the attachment connection. Here are some key load-bearing considerations:
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: Select a structural thermal break for masonry shelf angles attachment connections with high load-bearing capacity to ensure structural integrity is maintained. Typically, high-load capacity structural thermal breaks are the best solution for a masonry shelf angle application due to their strong mechanical properties that aid long term stability.
- Engineering Assessment: Conduct a structural analysis of the building to determine the appropriate size, thickness, and spacing of masonry shelf angles. Also, consider design factors such as the movement of the brick veneer, shrinkage of the framing, and code adherence. Assess the loads imposed by the masonry and ensure that the chosen shelf angle and structural thermal break can adequately withstand any forces at the attachment connection.
- Bolts: Properly fix masonry shelf angles and structural thermal breaks to the structural framing of the building. Bolt-through connections provide an adequate method for structural integrity and timely installation. (See “Bolt Selection and Improvements” above)
- Optimal Spacing: Determine the optimal spacing between the fixing locations of the shelf angle and the structural framing. Load-bearing and thermal performance requirements should be considered when determining the spacing. The more fixing locations, the worse the thermal performance can occur due to extra unwanted heat flow. However, this becomes redundant when ensuring the connection is structurally sound. By design, structural thermal breaks provide the necessary capabilities to satisfy both structural and thermal requirements for the majority of masonry shelf angle connections.
Simple Installation
Structural thermal breaks for masonry shelf angles are prefabricated to project requirements to ensure easy installation. The thermal breaks will be cut to size, predrilled, and individually marked so they can be easily identified on the job site. They are installed at bolt-through connection locations between the shelf angle and the structural framing; the thermal break does not have to run continuously with the shelf angle.
Information Required for Pricing
To provide an accurate structural thermal break quotation for your masonry shelf angle applications, the following information is needed:
- Quantities
- Dimensions
- Thickness
- Hole Size(s)
Quantity Note: The total linear footage divided by the spacing of the bolts will provide the structural thermal break quantities for your project.
If you do not have the required information for pricing, you can upload details here for a structural thermal break expert to provide clarity on your project details.